ភាពខុសគ្នារវាង "Concurrency" និង "Parallelism"
ក្នុងពិភពវិទ្យាសាស្ត្រកុំព្យូទ័រ ពាក្យ “concurrency” និង “parallelism” ពាក្យទាំងពីរនេះត្រូវបានគេប្រើប្រាស់ឆ្លាស់គ្នាជាញឹកញាប់ ប៉ុន្តែពាក្យទាំងពីរនេះគឺមានអត្ថន័យនិងគោលដៅពីរផ្សេងគ្នា។ ការយល់ដឹងអំពីភាពខុសគ្នារវាងពាក្យទាំងពីរនេះគឺមានសារៈសំខាន់ណាស់សម្រាប់អ្នកអភិវឌ្ឍន៍កម្មវិធីកុំព្យូទ័រ និងសម្រាប់អ្នកដែលចង់ស្វែងយល់ថាតើកុំព្យូទ័រអាចគ្រប់គ្រងនិងដោះស្រាយកម្មវិធីដែលដំណើរការជាច្រើនក្នុងពេលតែមួយដោយរបៀបណា។
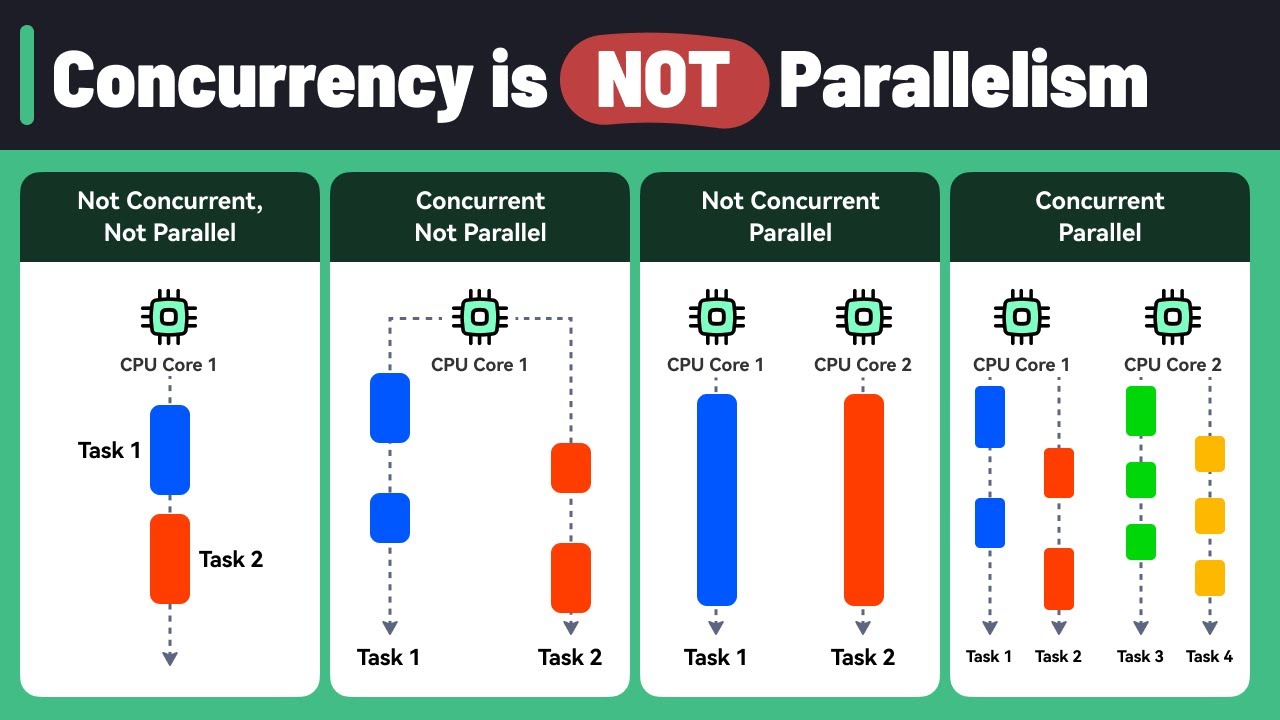
Concurrency: ការគ្រប់គ្រងនិងធ្វើកិច្ចការច្រើនក្នុងពេលស្រប់គ្នា
អ្នកទាំងអស់គ្នាអាចស្រមៃទៅមេចុងភៅម្នាក់នៅក្នុងផ្ទះបាយ។ ជាទូទៅមេចុងភៅមិនប្រើប្រាស់ពេលវេលារៀបចំម្ហូបតែ១មុខពីដើមដល់ចប់ទេ គាត់អាចផ្លាស់ប្តូរធ្វើនេះបន្តិចធ្វើនោះបន្តិចសម្រាប់ម្ហូបច្រើនមុខក្នុងពេលស្រប់គ្នា។ ជាឧទាហរណ៍ ក្នុងពេលដែលគាត់កំដៅទឹកស៊ុប ជៀសជាងប្រើពេលរង់ចាំទឹកស៊ុបនោះអោយឆ្អិនដោយមិនធ្វើអ្វីផ្សេង គាត់ប្រើប្រាស់ពេលវេលានោះដើម្បីរៀបចំគ្រឿងផ្សំសម្រាប់ម្ហូបមួយទៀត ឬក៏អាចផ្លាស់ប្តូរទៅរៀបចំបន្លែផ្សេងៗ ទាំងនេះបង្ហាញអោយយើងឃើញថានោះគាត់មិនទុកអោយពេលវេលានិងកំលាំងអោយខាត់ទទេដោយផ្លាស់ប្តូរទៅធ្វើការងារផ្សេងទៀត។ នេះហើយគឺជា “Concurrency”។

នៅក្នុងកុំព្យូទ័រ “Concurrency” គ្នាមានន័យថា ការប្រើប្រាស់កុំព្យូទ័រដើម្បីអោយកម្មវិធីច្រើនអាចដំណើរការលើកិច្ចការច្រើនជាងមួយគ្នាក្នុងពេលតែមួយស្រប់គ្នា ប៉ុន្តែមិនមានន័យថាវាចាំបាច់អោយប្រតិបត្តិក្នុងពេលដំណាលគ្នាទេ។ កិច្ចការទាំងនោះឆ្លាស់គ្នាប្រើប្រាស់ធនធានរបស់កុំព្យូទ័រ (ដូចជា CPU ដែលជាខួរក្បាលនៃកុំព្យូទ័រ)។ ដូចជាការចែករំលែកពេលវេលាសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ CPU ទៅវិញទៅមកសម្រាប់ប្រតិបត្តិកិច្ចការណាមួយ។
Parallelism: ការគ្រប់គ្រងនិងធើ្វកិច្ចការច្រើនក្នុងពេលតែមួយ
ប្រើប្រាស់ឧទាហរណ៍ខាងលើដដែរអ្នកទាំងអស់គ្នាអាចស្រមៃថាបើសិនជាយើងមានមេចុងភៅជាច្រើននាក់នៅក្នុងផ្ទះបាយធំមួយ ដោយគាត់ម្នាក់ៗធ្វើការលើការកុម្ម៉ង់ម្ហូបផ្សេងៗគ្នាក្នុងពេលតែមួយ។ មេចុងភៅម្នាក់អាចកំពុងតែហាន់បន្លែ ម្នាក់ទៀតកំពុងតែអាំងសាច់ ហើយចុងភៅផ្សេងទៀតអាចធ្វើការងារផ្សេងៗទៀត - សកម្មភាពទាំងអស់នេះគឺកើតឡើងក្នុងពេលតែមួយដំណាលគ្នា។ នេះគឺជា “Parallelism”។

នៅក្នុងកុំព្យូទ័រ “Parellelism” មានន័យថា កម្មវិធីមួយអាចបំបែកកិច្ចការរបស់ខ្លួនទៅជាកិច្ចការរងច្រើនផ្សេងគ្នា ហើយដាក់អោយកិច្ចការទាំងនោះដំណើរការក្នុងពេលដំណាលគ្នា (ដូចជាប្រើប្រាស់ CPU ពីរឬច្រើនក្នុងពេលតែមួយ)។ ការប្រតិបត្តិការនេះទើបជាការធ្វើកិច្ចការច្រើនក្នុងពេលតែមួយស្របគ្នាពិតប្រាកដហើយក៏នាំឱ្យបញ្ចប់ការងារទាំងមូលលឿនជាងមុនផងដែរ។
សង្ខេបពីភាពខុសគ្នា:
- Concurrency: ការគ្រប់គ្រងកិច្ចការច្រើនអោយដំណើរការស្របគ្នាដោយធ្វើការឆ្លាស់គ្នាក្នុងការប្រើប្រាស់ធនធានរបស់កុំព្យូទ័រ។
- Parellelism: ការអនុវត្តកិច្ចការងារច្រើនក្នុងពេលដំណាលគ្នាដោយប្រើប្រាស់ធនធានរបស់កុំព្យូទ័រពីរឬច្រើន។
ហេតុអ្វីបានជាចំបាច់យល់អំពីអត្ថន័យរវាងពាក្យទាំងពីរនេះ?
ការយល់ដឹងអំពីភាពខុសគ្នារវាង “Concurrency” និង “Parallelism” គឺសំខាន់សម្រាប់៖
- ការរចនាកម្មវិធីដែលអោយមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព: ការជ្រើសរើសវិធីសាស្រ្តត្រឹមត្រូវសម្រាប់ការដោះស្រាយប្រតិបត្តិការច្រើនអាចជះឥទ្ធិពលយ៉ាងខ្លាំងដល់ដំណើរការនៃកុំព្យូទ័រ។
- ការប្រើប្រាស់ផ្នែករឹង (Hardware) ឱ្យមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព: “Parallelism” អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យកម្មវិធីអាចប្រើប្រាស់ថាមពលពេញលេញនៃប្រព័ន្ធដំណើរការនៃពហុស្នូល។
- ការបង្កើតកម្មវិធីដែលឆ្លើយតបបានល្អនិងរហ័ស: “Concurrency” អាចជួយការពារកម្មវិធីពីការគាំងនៅពេលអនុវត្តកិច្ចការដែលត្រូវការប្រើពេលយូរ។
នៅក្នុងកុំព្យូទ័រក្នុងសម័យទំនើប យើងច្រើនតែឃើញការប្រើប្រាស់រួមបញ្ចូលគ្នារវាង “Concurrency” និង “Parallelism” ដែលវាជាផ្នែកមួយធ្វើអោយកម្មវិធីរបស់យើងដំណើរការដោយមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព និងឆ្លើយតបបានរហ័សល្អទៅកាន់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់កម្មវិធី។